Mast Cell Degranulation Assays
Human Mast cell Assays
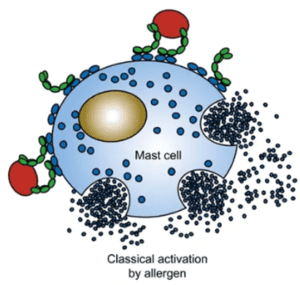
Mast cells, distributed in connective tissues across the body, are crucial regulators of immune responses. They play a dual role — maintaining homeostasis and promoting repair, while also being implicated in allergy, asthma, anaphylaxis, gastrointestinal disorders, cancer, and cardiovascular disease.
Mast cells express c-Kit and FcεRI receptors and can be categorized into mucosal and connective tissue subtypes, each releasing a wide range of inflammatory mediators such as histamine, cytokines, proteases, and neutral proteases. Their activation through IgE/FcεRI cross-linking or stem cell factor signaling makes them a key target for both basic research and therapeutic applications.
Human Primary Mast Cell Degranulation Assays
Our primary mast cell assays are widely applied to study disease biology, including:
Allergy and anaphylaxis
Asthma and IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions
Mastocytosis and mast cell activation syndromes
Anti-helminth immunity
Cancer immunology
These assays enable precise monitoring of mast cell activation and mediator release, supporting drug discovery and translational research.
Challenges of Mast Cell Research
✅ Primary human mast cells are rare, with limited availability from peripheral blood and tissues
✅ Differentiation of precursor cells to mast cells is time-intensive and costly
✅ Many mast cell lines exhibit altered phenotypes, lacking critical receptors (FcεRI) or showing impaired cytokine production
Our Service Features
✅ Flexible models: Primary human CD34+ blood-derived mast cells or RBL-2H3 cell lines
✅ Comprehensive readouts: histamine release, β-hexosaminidase, cytokines, PGD2, gene expression, and degranulation induction assays
✅ High throughput capability: 96- and 384-well formats with replicates, enabling multiplex transcriptomic and proteomic analysis
✅ Robust and reproducible: validated protocols and high-quality reagents ensure consistent, reliable results

How Does Our Assays Work
✅ Isolation of CD34+ precursor cells from peripheral blood
✅ Differentiation into mature mast cells
✅ Evaluation of purity (c-Kit and FcεRI expression)
✅ Test compound treatment under stimulation
✅ Readout quantification: cytokine release, gene expression, histamine and degranulation markers
Example Data (a)
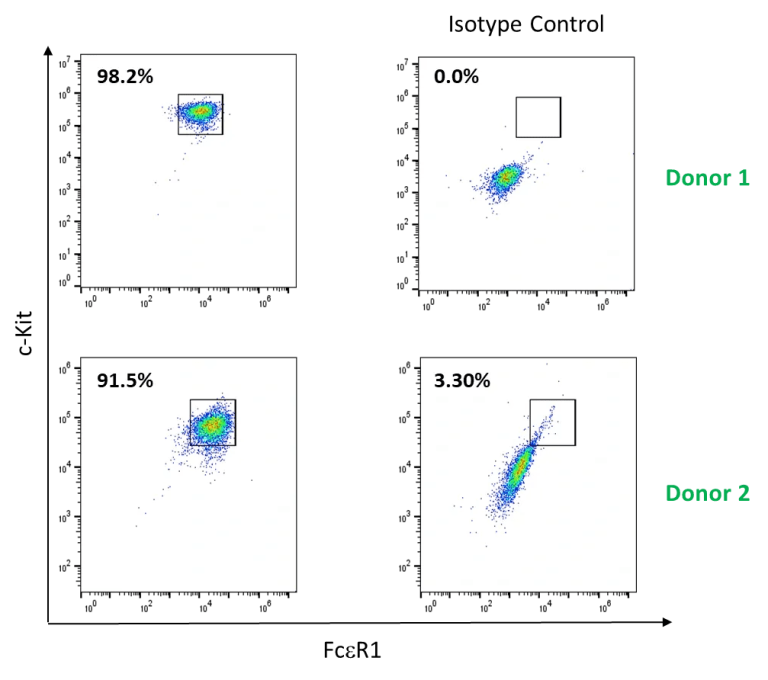
Primary CD34+ hematopoietic precursor cells isolated from 2 healthy donors were differentiated to mast cells in vitro by culturing cells in medium supplemented with recombinant stem cell factor (SCF), interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-3. Mast cell culture purity was evaluated after weeks of differentiation based on the expression of c-kit and FcεR1 with flow cytometry.
Example Data (b)
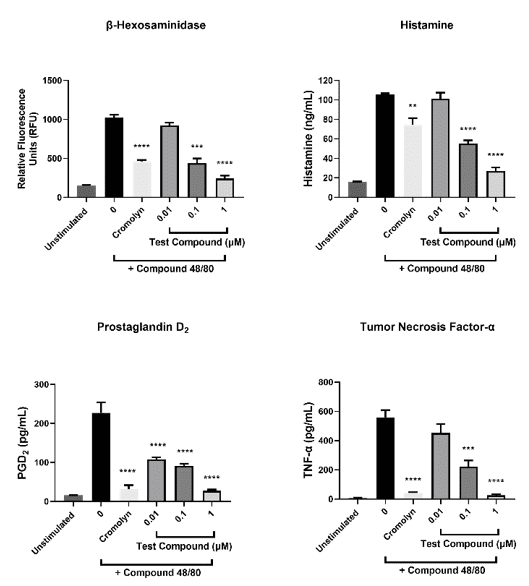
Mature CD34+ hematopoietic precursor-derived mast cells were incubated with varying concentrations of test compound or cromolyn (mast cell stabilizer) during stimulation with compound 48/80 (mast cell activator). After treatment, β-hexosaminidase, histamine, prostaglandin D2 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in the cell-free supernatants were quantified. Data shown are mean ± SEM (3 donors).