Neutrophil, Basophil & Eosinophil Assays
Human neutrophil assays
Neutrophils are the most abundant leukocytes in blood and act as the body’s first line of defense. They employ phagocytosis, degranulation, and NETosis (neutrophil extracellular trap formation) to eliminate pathogens. Beyond host defense, neutrophils influence both innate and adaptive immunity and are increasingly linked to disease progression in thrombosis, gout, atherosclerosis, and cancer.
Our neutrophil assay services include:
Neutrophil isolation or whole blood collection
Purity evaluation (CD66b, CD16 expression)
Test compound treatment and functional stimulation
Readout quantification: ROS generation, NETosis, phagocytosis, degranulation
These assays enable mechanistic insights into neutrophil biology and help identify novel therapeutic strategies.
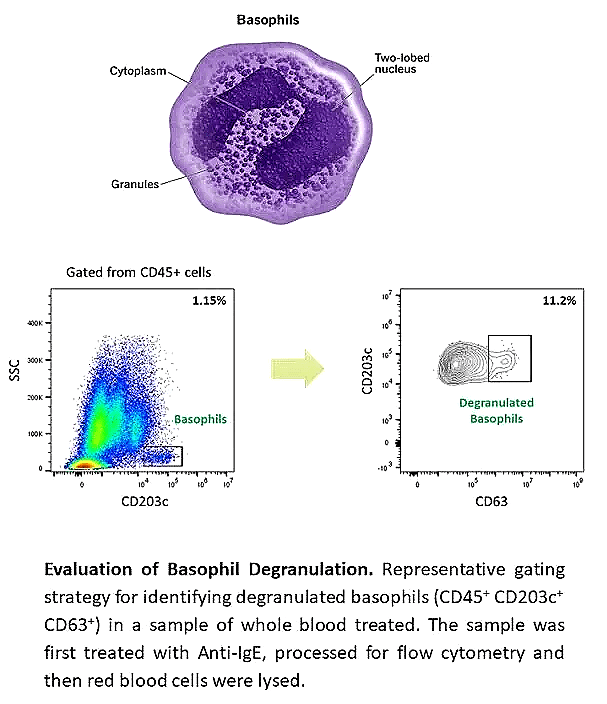
Human Basophil Assays
Basophils are rare but critical granulocytes involved in type 2 immune responses. They circulate as mature cells, respond to IgE-FcεRI crosslinking, and release cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-13. Their role in allergic inflammation makes them valuable models for allergy research and clinical testing.
Our basophil assay services include:
Basophil Activation Test (BAT) to evaluate immune responses by flow cytometry
Analysis of activation markers (CD123, IgE, CD63, CD203c)
Quantification of degranulation and cytokine release
BAT applications:
In vitro models for allergy drug discovery
Biomarker of clinical response to treatment
Exploring mechanisms of allergic disease at the effector cell level
Confirming patient eligibility for allergy therapy
Human Eosinophil Assays
Eosinophils are granule-rich immune cells involved in host defense and inflammatory disease. Their cytotoxic proteins and cytokines protect against helminths but also contribute to asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis, pulmonary disease, and colitis. Given their dual role in immunity and pathology, eosinophils are a critical target for therapeutic discovery.
We provide tailored assays to study eosinophil function and compound effects.
Typical workflow includes:
✅ Isolation & Purity Check
Primary eosinophil isolation from whole blood;
Purity evaluation (CD66b, CD16 expression)
✅ Compound Treatment
Direct test compound exposure;
Optional stimulation with agents such as:
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA, A-23187)
Cytokines (IL-4, IL-13, Eotaxin);
Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF)
✅ Readout Quantification
Extracellular trap formation;
Degranulation (eosinophil peroxidase release);
Cytokine production (IL-3, IL-9, IL-13, IL-5, GM-CSF, FGF, PDGF, CCL5, CCL11, CCL17, etc.)
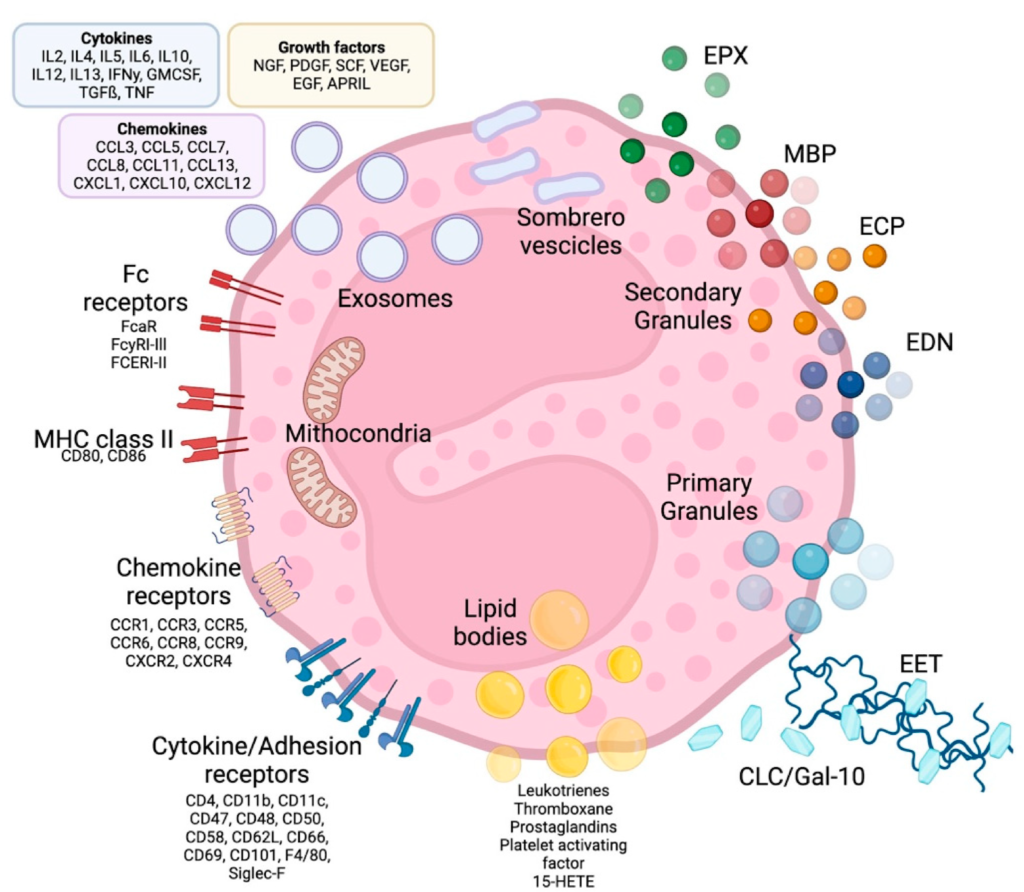
CLC/Gal-10: Charcot-Leyden Crystal Proteins; ECP: Eosinophil Cationic Protein; MBP: Makor Basic Protein; EPX: Eosinophil Peroxidase; EDN: Eosinophil-derived Neutotoxin; EET: Eosinophil Extracellular Traps; MHC: Major Histocompatibility Complex
Example Data
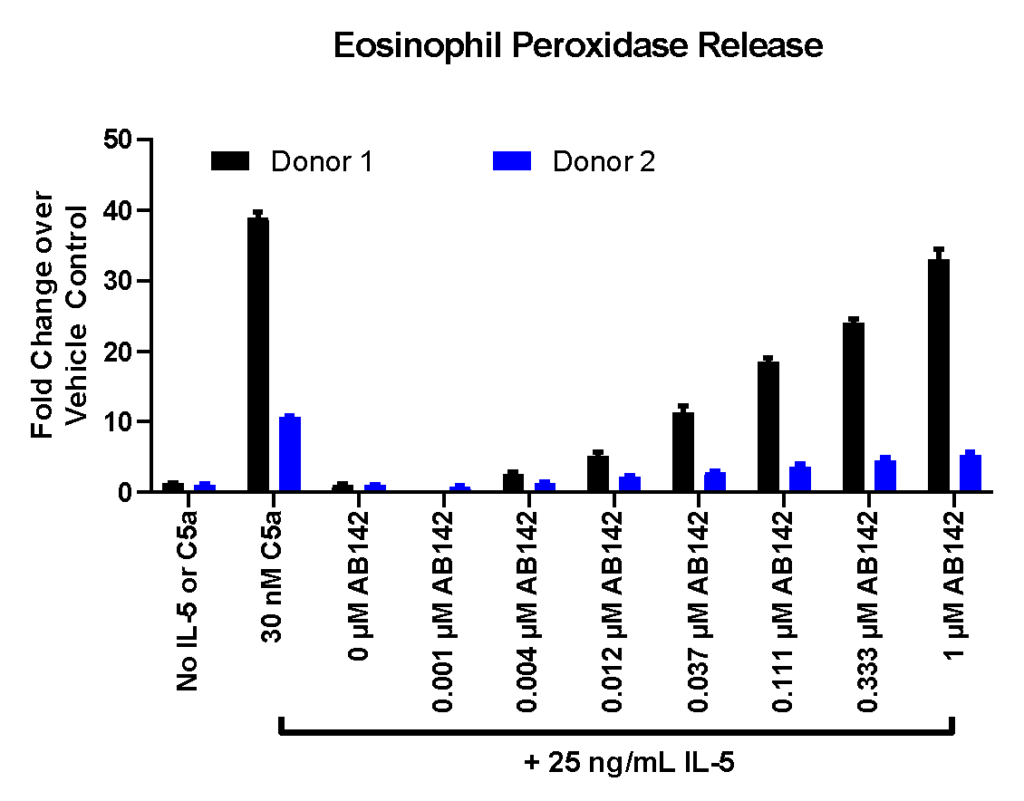
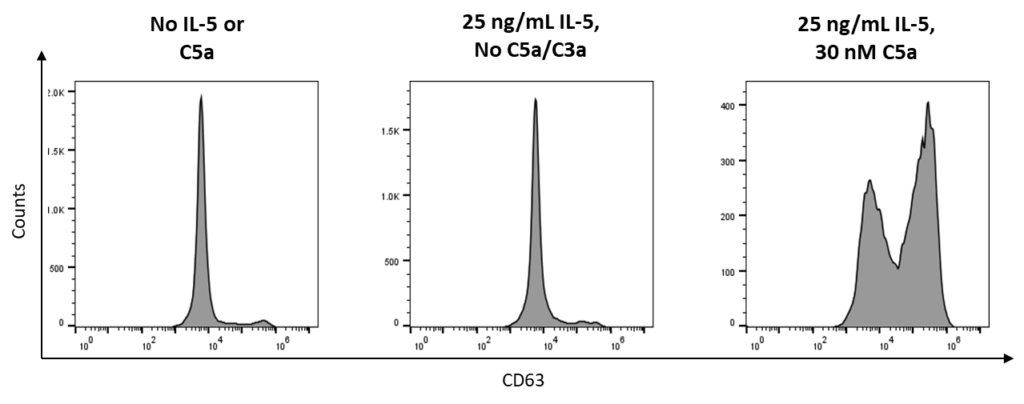
Effect of Test Compound on Eosinophil Degranulation. IL-5-primed human eosinophils were treated with C5a (positive control) and several concentrations of test compound AB142. Degranulation was evaluated by eosinophil peroxidase release and CD63 expression. (A) Representative flow cytometry plots showing CD63 expression after each control treatment condition. (B) EPX release following various treatment conditions. Data are represented as fold of change over vehicle.