T Cell Functional Assays
T Lymphocytes & T Cell Activation
T cells are central to adaptive, cell-mediated immunity. Originating in the bone marrow and maturing in the thymus, they differentiate into helper, regulatory, cytotoxic, or memory subsets. Upon encountering specific antigens, T cells are activated through a multi-signal process involving antigen recognition, costimulatory signaling, and cytokine release. Activated T cells regulate immune responses, support B cell activity, and directly eliminate infected or malignant cells.
At Axela, we provide a wide array of functional T cell assays to support immunology research, oncology, and drug development. Our expertise spans antigen-specific responses, checkpoint modulation, cytokine profiling, and advanced cytotoxicity models.
Our Services Include:
💠Activation & Proliferation Assays
Mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR)
Anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation, PMA/Ionomycin, SEB, checkpoint blockade (anti-PD1, anti-CTLA4)
High-throughput flow cytometry and readouts (CFSE, BrdU, DELFIA)
💠Cytotoxicity & Response Assays
T cell-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (TDCC), including bispecific T cell engager (BiTE) assays
Tumor killing assays (TKA)
γδ T cell cytotoxicity assays
3D spheroid T cell-mediated cytotoxicity
💠Checkpoint & Exhaustion Studies
Immune checkpoint blockade assays
T cell exhaustion and reversal assays
T cell differentiation and suppression assays (Treg/MDSC functional profiling)
💠Cytokine & Phenotypic Profiling
Cytokine secretion (ELISA, Luminex, AlphaLISA, Lumit, ELISpot)
IL-2 and signaling assays (phospho-Flow, pSTAT5, etc.)
T cell surface marker expression (flow cytometry)
Chemotaxis and migration assays
💠Specialized Assays
On/Off target testing for TCR and cellular therapeutics
TAA-specific T cell response assays
Immune synapse formation assays
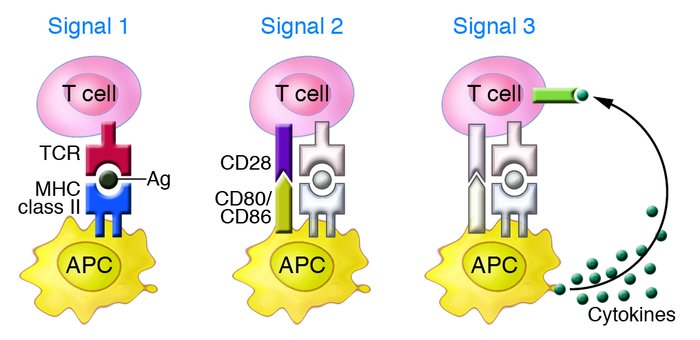
T cell activation requires three distinct signals provided by antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
Signal 1: Antigen recognition via the T cell receptor (TCR) binding to antigen–MHC complexes.
Signal 2: Costimulatory signaling through molecules such as CD28 and CD80/CD86.
Signal 3: Cytokine release from APCs, which drives T cell proliferation, differentiation, and effector functions.
Mixed Lymphocyte Reaction (MLR) Assay
MLR assay evaluates compounds that influence the interaction between antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and T cells, enabling assessment of T cell activation, deactivation, or reprogramming. It provides key insights into the efficacy of immunomodulatory agents and drug safety in immunology, oncology, and autoimmunity.
Axela’s MLR platform supports rapid identification of T cell–modulating agents, suitable for both biologics and small molecules. Using ultrassensitive immunoassays, multiplex cytokine profiling, and advanced flow cytometry, we deliver high-quality analysis across multiple endpoints, including proliferation, cytokine release (e.g., IL-2, IFN-γ), and cell-surface marker expression.
One-way MLR: Responder lymphocytes (e.g., CD4+ T cells) from one donor are stimulated by mitomycin C–treated stimulator cells (e.g., DCs) from another donor.
Two-way MLR: Lymphocytes from both donors stimulate each other, modeling broader allogeneic responses.
Our Services Include:
High-throughput format: 96–384 well plates
Robust, reproducible assays suitable for small to large-scale studies
Flexible design for single-agent or combination testing
Access to multiple allogeneic donors (PBMCs, CD3+/CD4+ T cells, monocyte-derived DCs)
Multiparametric readouts: cytokines, proliferation, and surface markers
State-of-the-art platforms: Luminex-200, FlexMAP 3D, CytoFLEX S flow cytometer (13-color, 4-laser)
Fast turnaround: quantitative results in as little as 4 weeks
Fully validated and quality-controlled with triplicate replicates
Comprehensive controls: isotype IgG, inhibitors, and stimulators
Over 20 years of hands-on expertise with expert analysis and reporting
Example Data
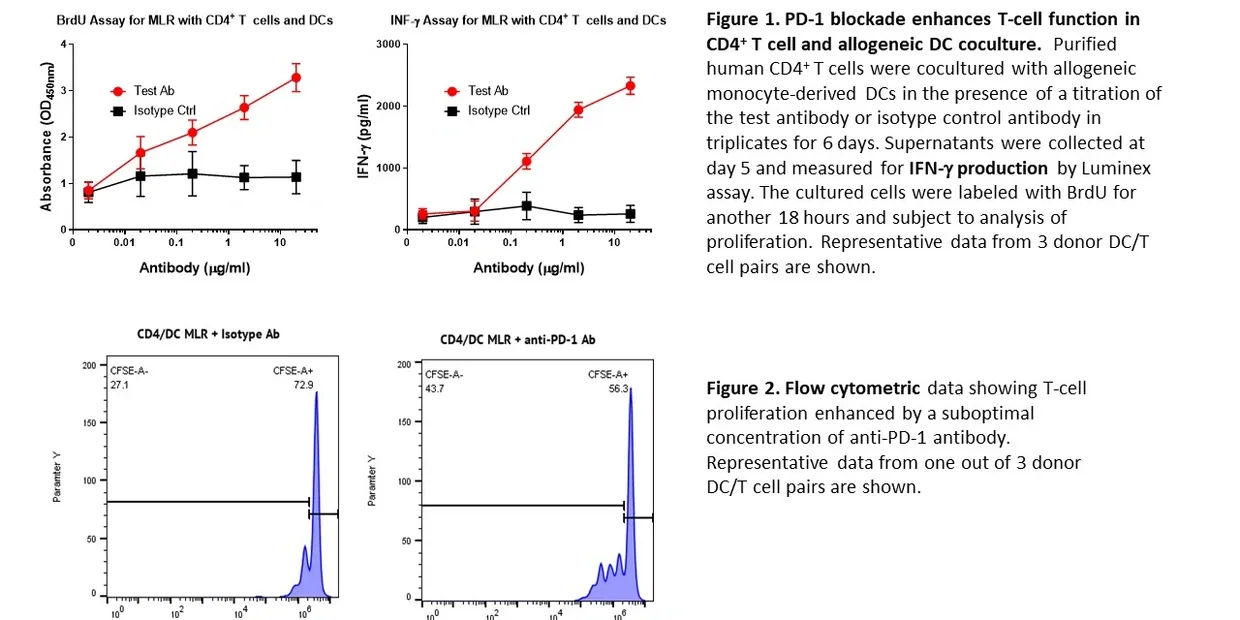
T Cell Activity Assay Example Data:
Representative data showing the effect of PD-1 blockade on T cell proliferation and cytokine production in a mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR). Human CD4⁺ T cells were cocultured with allogeneic monocyte-derived dendritic cells (DCs) in the presence of either test antibody or isotype control.
Figure 1: BrdU incorporation and IFN-γ secretion demonstrate that anti-PD-1 treatment enhances both T cell proliferation and cytokine production compared to controls.
Figure 2: Flow cytometry analysis confirms increased proliferation of CD4⁺ T cells when treated with anti-PD-1 antibody.
These results highlight how MLR assays can be used to assess immunomodulatory activity and quantify functional enhancement of T cell responses.